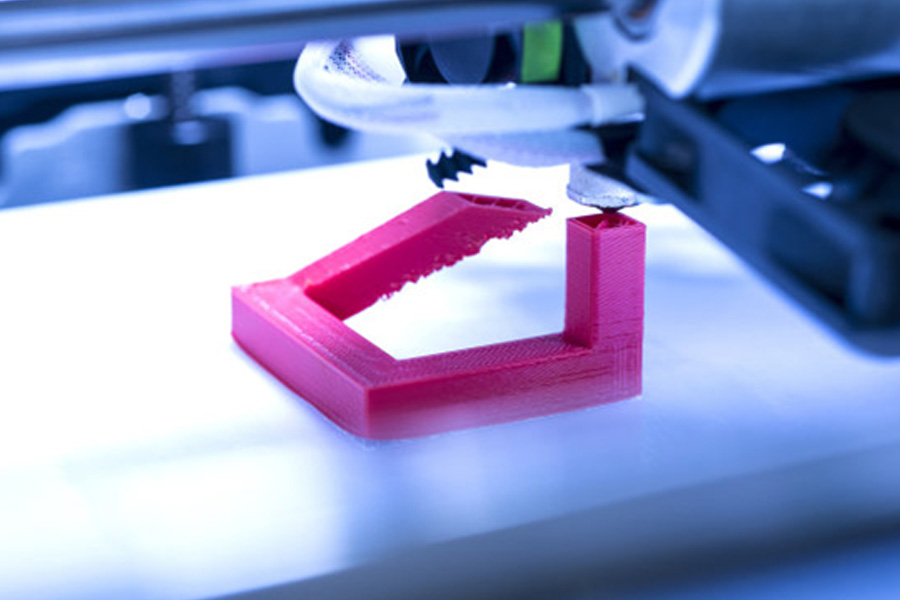
3D printing technology is regarded by some manufacturing companies as one of the internal driving forces of “Industry 4.0”, and this technology has also begun to be more widely used in the automotive field. Recently, BASF 3D Printing Solutions Co., Ltd. (B3DPS) demonstrated a 3D printed engine bracket that attracted the attention of the industry. It is reported that this product was developed in cooperation between BASF and Daimler.
According to reports, this engine bracket uses the polyamide series material Ultrasint® PA6 MF. This material has good rigidity and can show excellent printing performance on high-temperature printers. In the past, it was difficult to adapt to a wide range of requirements to produce engine brackets according to traditional molds, and could not be matched with various types of automobiles, and the entire production process was time-consuming and costly. If 3D printing technology is used to produce car brackets, time-saving, high-efficiency and safety can be achieved. In addition, 3D printing technology has also created conditions for the entire automotive industry to realize automated and intelligent manufacturing transformation.
Daimler expects that 3D printing technology will improve its ability to manufacture medium-sized parts, and there are no costs related to manufacturing or purchasing tools, and there is no need to hire additional production line workers, which can save up to 50% compared with current manufacturing methods. %the cost of. In fact, other automakers are gradually adopting 3D printing technology to produce small-scale components with more complex structures, including some molds and prototypes. For example, General Motors uses 3D printing technology to make tools for its factories; Ford will use 3D printed parts in the new Shelby GT500.