3D printing has many relationships with injection molding. Through this article, you can understand why there are 3D printed injection molds and the manufacturing process.
To understand what a 3D printed injection mold is, we start with conventional injection molding.
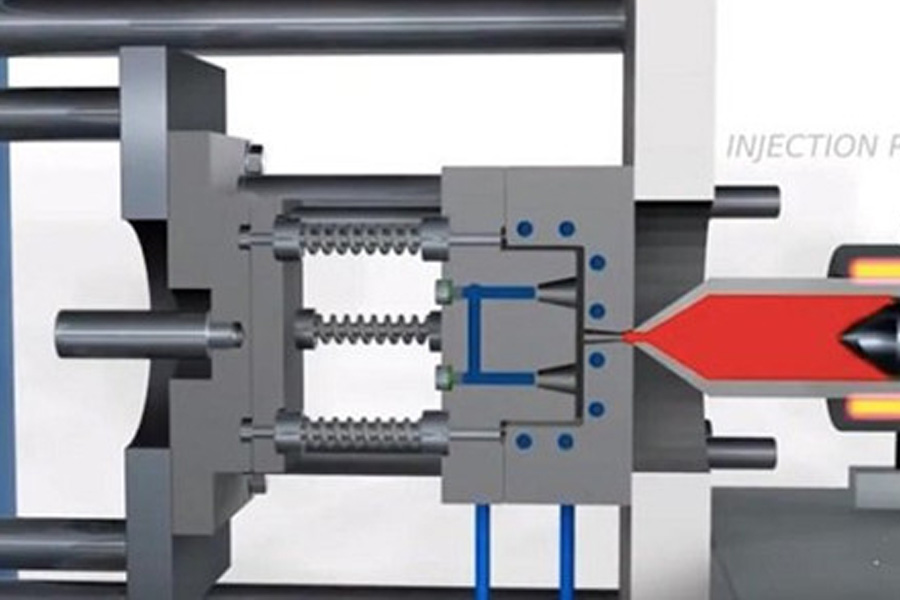
Injection molding is one of the most common manufacturing processes in the plastics industry. Essentially, molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity so that it hardens as it cools, then the mold is opened and the plastic part is taken out. Injection molding is mainly used for mass production because of its high upfront cost in design, testing, and processing. Of course, the more parts are produced, the unit price will drop sharply. This is the reason and advantage of using injection molding for mass production.
Why 3D printing?
The injection mold itself is a metal block with cavities that determine the shape of the finished product. Traditionally, molds are designed and produced by computer numerical control (CNC) milling machines, which are very expensive. Since molds are usually made of metals such as steel and aluminum, they are difficult to change once they are produced. Therefore, 3D printing injection molds provide a cheap and flexible alternative. Let’s take a look at how to actually print 3D injection molds, pros and cons, new developments in 3D printing injection molds, and the final printing techniques.
Note: Although many people can do 3D printing injection molds, in actual use, more energy and equipment may be required. Of course, professional 3D printing services can also be used.
How to 3D print molds?
data processing
3D printing injection moulding is similar to printing other 3D printing objects:
- The injection mold is designed using CAD software, such as AutoCAD or Fusion 360.
- The design file is saved in STL format and sliced into G code.
- Use a 3D printer to print the mold layer by layer.
- Install the mold into the metal frame and prepare for injection.
Materials for 3D printing injection molds Now that the basic process of 3D printing injection molds has been introduced, let’s take a look at which materials can be used. Generally speaking, you need a product with high strength and rigidity to withstand the pressure generated during the injection process. Moreover, it will need to be resistant to high temperatures.
The following are several commonly used materials for 3D printing injection molds:
- PETG (polyethylene terephthalate)
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- Nylon (also known as polyamide)
- PP (polypropylene)
- TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)
- POM (polyoxymethylene, also known as Delrin or acetal)
SLM, SLA, FDM, material jetting and SLS can be used to complete 3D printing injection molds. In other words, due to the high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface that are very suitable for injection molds, SLA is the preferred 3D printing method for producing injection molds.
There is one thing you should know about metal frames and their role in injection molds. The frame provides support for the pressure and heat generated during the injection molding process. Since the metal frame can be used universally, only the core part of the mold needs to be 3D printed, so it is easy and flexible to change the design. However, in the case of 3D printing of the entire mold, more materials and longer printing time are required.
Advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing injection molds
3D printing is an excellent choice for producing injection molds, but it also has its drawbacks. 3d-printing-china.com specially reminds that the following comparison excludes metal 3D printing molds.
advantage
Low cost: The traditional method of producing injection molds is very expensive and time-consuming, requiring precision machinery and expertise from the mold maker. And 3D printing is a cheaper method of making molds. According to reports, compared with traditional technology, 3D printing molds can save up to 80% of the cost.
Flexibility and efficiency: 3D printing greatly reduces design and production time. Anyone with 3D printing experience can print the mold, and if you are not satisfied with it, you can simply adjust the design and print another one.
Applicability of small batch production: The initial cost of injection molds made by traditional methods (such as CNC milling) is high. Therefore, it is only cost-effective when the output is large enough. On the other hand, the manufacturing cost of 3D printing molds is much cheaper, and if there is no high initial cost in the early stage, it is best to use 3D printing molds to complete small and medium batch production.
shortcoming
- Longer production time: Since the thermal conductivity of plastic is lower than that of metal, it takes longer for 3D printed plastic molds to produce products, thereby prolonging the overall production time and reducing productivity.
- Shrinkage: Like many other 3D printed objects, 3D printed injection molds may shrink when cooled, which is a common problem in 3D printing. This can cause problems when precise dimensions are required.
- Weak structural integrity: Most 3D printing molds are made of plastic and cannot withstand high temperatures and pressures for a long time. This will cause the 3D printed injection mold to age at the gate and weld.
Cutting-edge research on 3D printing injection molds
Let’s take a look at some of the latest developments in the field of 3D printing injection molds.
Surface coating
3D printed injection molds are prone to degradation under high temperature and high pressure. Improving surface life with protective coatings is one way to prevent thermal degradation. Depositing a layer of metal, metal nitrate, ceramic and oxide on the surface of a 3D printed injection mold can enhance its heat resistance and tear resistance.
Thermally conductive composite
Thermal conductivity is a measure of the thermal conductivity of an object. Metal has better thermal conductivity than plastic. In other words, metal can be heated or cooled faster than plastic. Since 3D printed injection molds (molds) have longer heating and cooling stages than CNC molds, their cycle time is also longer. Only a few products can be produced in a given period, and the production cost will increase compared with traditional metal molds. In order to solve this problem, a thermal conductivity additive was added to the mold material to improve the injection process. For example, boron nitride can be added to ABS, and iron particles can be added to epoxy resin.
Metal 3D printing injection mold
Metal has better thermal conductivity than plastic, so why not 3D print metal injection molds? With the latest development of metal 3D printing, this has also begun to receive a large number of applications. However, 3D printing metal is still much more expensive than plastic, so the upfront cost is still high.
Precautions for 3D printing injection molds
Before you start printing injection molds, consider the following useful tips:
Number of prints: make sure you know how many products you want to make! Keep in mind that 3D printed injection molds are only used for small batch production (30 to 100 pieces, depending on the mold). Therefore, if you plan to manufacture thousands of them, you may want to consider using regular molds.
Add draft angle: a right angle will make it difficult to eject the injection part from the mold, so try to add a 2 degree draft angle to make the object easier to slide out.
Use 3D printing service: Don’t forget that there is always a 3D printing service route, which can help you design molds and print molds according to your exact requirements without any effort. There are many such service providers in China.
This article is reproduced from: https://3d-printing-china.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-non-metallic-3d-printing-injection-molds-is-here/



