Introduction: stl files are currently popular files for 3D printing. Now, this file format is gradually being replaced by the 3MF format.
STL is a relatively “old” 3D file format. It was first released by 3D Systems in 1987. It is an acronym for Stereolithography. The stl file is designed to take into account the situation of additive manufacturing, and the data (usually based on NURBS or BREP) is converted into a grid for analysis by a 3D printer. Therefore, curves and compound surfaces are converted into code that runs on machine data. STL uses small triangles to simulate the original surface of the model. The more complex and detailed the structure, the more triangles are needed.
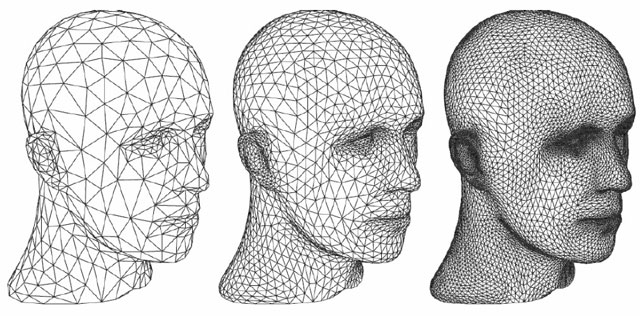
△The more complex and detailed the structure, the more triangles used.
“Traditional” stl file
The stl file describes the original, unstructured triangulated surface by using the unit normals and vertices of the triangles of the three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system (sorted according to the right-hand rule). The natural file format of this machine is a series of closed polygons (layers or slices) corresponding to different Z values. However, since the layer thickness can be changed, STL can perform simulations in a faster but less precise construction method, defining the construction model as a collection of closed polyhedrons sliced in the horizontal plane. However, STL is based on a grid architecture after all, and cannot store information as mathematical expressions. Therefore, only the original information can be carried forward. This causes it to take up a large amount of hard disk space when storing, while not causing damage to the geometric structure of the model itself.
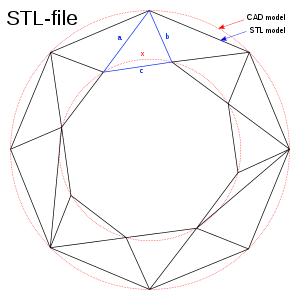
△Under the same shape, the CAD format appears as a ring (shown as two concentric red circles), while the STL is composed of a triangular plane.
In addition, STL does not carry any machine information, print settings or any other useful information needed to recreate files. Therefore, when working with a team or a third party to manufacture parts, it is necessary to attach the STL and the manufacturing specification list together. Despite various flaws, STL has become the most popular 3D printing file format for the following reasons:
- STL as a standard file format has a wide audience
- The 3D printer only supports the grid-based file format in the slicer
- There are too few alternatives and they are not popular
The rise of the 3MF format
3MF is a new file format developed by a consortium of companies that advance 3D printing capabilities and technology. It is considered a revolutionary and unique format. The improvements brought by 3MF are equivalent to switching from BMP to PDF: 3MF carries more information, including unit information, color and texture information for multi-inkjet printing, relative positions in space, and so on. STL has no unit. Even if the two file formats carry the same amount of data, the 3MF file is still much smaller than the stl file.
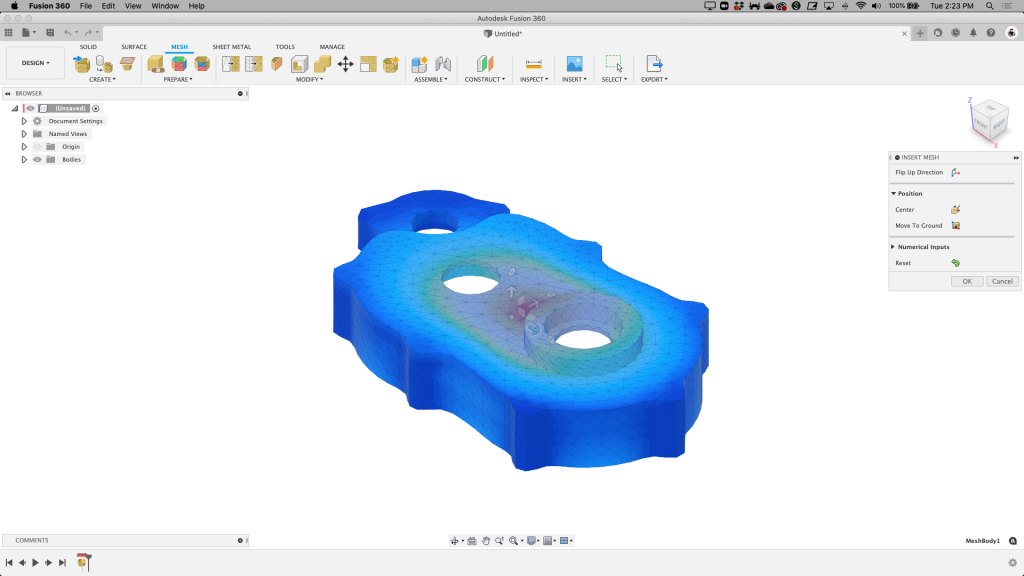
△Import the 3MF file of Fusion 360 grid workspace. There is no unit tab in the right dialog box because the 3MF file contains this information.
The 3MF file uses a human-readable XML format (Extensible Markup Language), so a large amount of data required for the machine can be stored, without the need for additional print settings in a separate file. Users can even open XML to read and perform operations and directly modify the code. This not only provides variety, helps prevent printing errors, but also helps reduce file size. 3MF does not need to repeat data when processing the same parts in batches, and even allows users to save and share desired slice configurations, saving time.
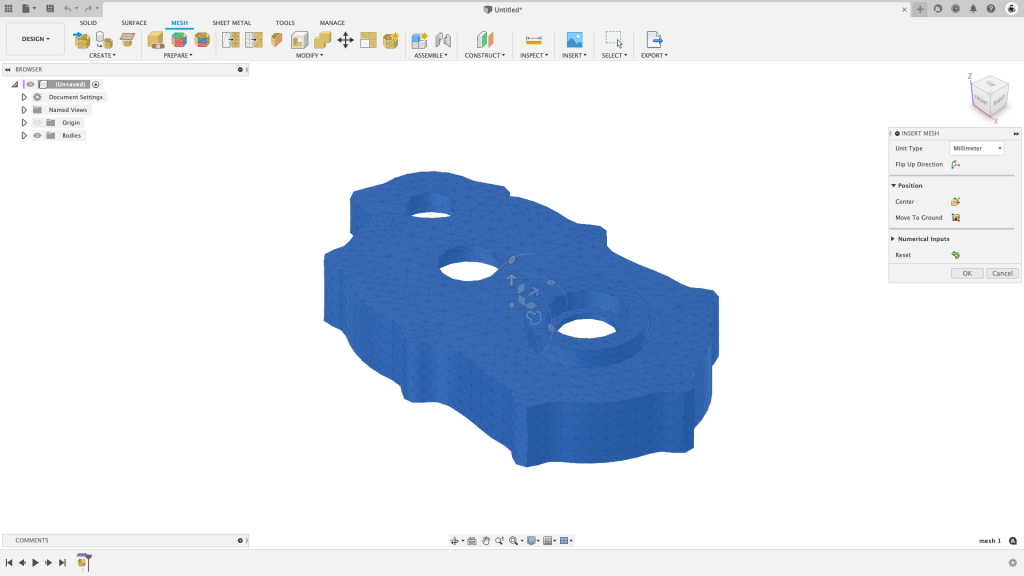
△The same data imported by STL lacks color information, and the dialog box needs user-defined unit size.
3MF can also display detailed information of parts:
- Describe the model completely and sufficiently richly, retaining internal information, color, location and other characteristics
- Scalable to support 3D printing innovation
- Interoperable
- Can be widely adopted
- Get rid of other common file format problems
When using the 3MF format with SLS, packaging information, number of copies of parts, and all initial data are contained in one file. This minimizes errors and ensures that anyone with the files can repeat your machine settings and part geometry.
The role of the manufacturing process
The 3MF format can carry metadata for print settings and machine information, which also requires a slicer independent of the specific machine. For example, the additive manufacturing space of Fusion 360 covers all the above settings and allows the export of STL and 3MF files. This can help users keep all manufacturing data in their place: centralize all relevant design data.
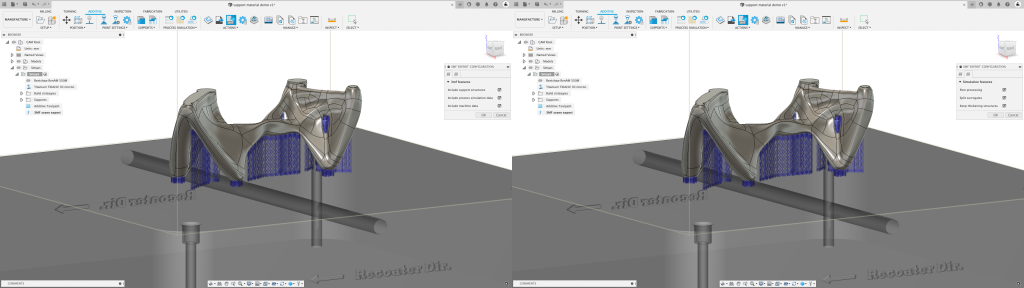
△The 3MF exported by Fusion 360 shows two tabs of metadata.
At the same time, access to print settings and machine information also means that you can fully control your support structure, and you can use a single file to transfer information to the printer. This is impossible for STL, unless additional optimization techniques are used. Finally, 3MF can also bring security protocols to manufacturing data, for example, it can limit the number of copies of machine-made parts. This secure content extension provides a mechanism for encrypting sensitive 3D printable data, helping to protect intellectual property, reduce risk, and ensure that companies comply with government regulations.
Other 3D printing file formats
In addition to STL, OBJ is also a very common file format, which can store texture and color information. The PLY format (Polygon format) is often used for 3D scanned object files. In addition, like 3MF, the AMF format is also an emerging 3D printing file format, which can record color information, material information, and internal structure of objects. It also uses XML format. Although AMF has the potential to become a new generation of 3D printing data standards, its lack of support from giants is its fault.